What is sleep apnea?
Sleep apnea is a disorder characterized by irregular pauses in breathing or instances of shallow breathing during rest. Each pause in breathing, called an apnea, can last from a few seconds to minutes, and may occur 30 or more times per hour.
Individuals with sleep apnea often experience daytime sleepiness, trouble concentrating, and mediocre performance at work or school. They may also suffer from mood swings and fatigue.
The disorder is a rather common occurrence; scientists estimate that 2% to 4% of adults in the U.S. have it, and it is more common among men than women.
The disorder can be treated with lifestyle changes, such as losing weight or quitting smoking, and with medications or surgery. Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy is the most common treatment for obstructive sleep apnea.

Types of Sleep Apnea
There are three main types of sleep apnea: obstructive, central, and mixed.
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most common type of sleep apnea and occurs when the muscles in the back of the throat relax and block the airway. This results in breathing pauses and snoring. OSA is generally caused by excess weight, allergies, a large neck size, and smoking. Treatment options include lifestyle modifications such as losing weight, avoiding alcohol, quitting smoking, and avoiding sleeping on your back.
Central sleep apnea (CSA) is a less common form of sleep apnea that occurs when the brain fails to send signals to the muscles that control breathing. This can cause a person to stop breathing for short periods of time. CSA is usually caused by medical conditions such as stroke, heart failure, or brain tumors. Treatment options include lifestyle modifications such as avoiding alcohol and sleeping on your side, as well as the use of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machines.
Mixed sleep apnea (MSA) is a combination of both obstructive and central sleep apnea. It is caused by a combination of factors such as obesity, stress, and medical conditions. Treatment options for MSA include lifestyle modifications such as losing weight, avoiding alcohol, and quitting smoking, as well as the use of CPAP machines.
Impact
If left untreated, sleep apnea can cause a variety of health issues, ranging from mild to severe.
The most common symptom of sleep apnea is loud snoring, which is caused by the obstruction of the airway during sleep. This disrupts the sleep cycle, causing the individual to wake up frequently throughout the night. This results in an overall decrease in quality of sleep, which can lead to daytime fatigue and exhaustion.
Sleep apnea can also have an impact on cardiovascular health. Many individuals with sleep apnea suffer from high blood pressure, an increased risk of stroke, and an increased risk of heart attack.
Sleep apnea can cause the body to produce more cortisol, a hormone that can raise the risk of diabetes and obesity. It can cause mental health issues. Sleep deprivation can cause irritability, trouble concentrating, and mood swings. Severe cases of sleep apnea can also increase the risk of developing anxiety and depression.
For those suffering from sleep apnea, CPAP is one of the most common treatments. It involves a machine that pumps air into the airway while the individual sleeps. Surgery is also an option for some individuals, though it is typically reserved for more severe cases. It is important for individuals with sleep apnea to seek treatment as soon as possible. Not only can it help improve their quality of life, but it can also prevent more serious health complications in the future.
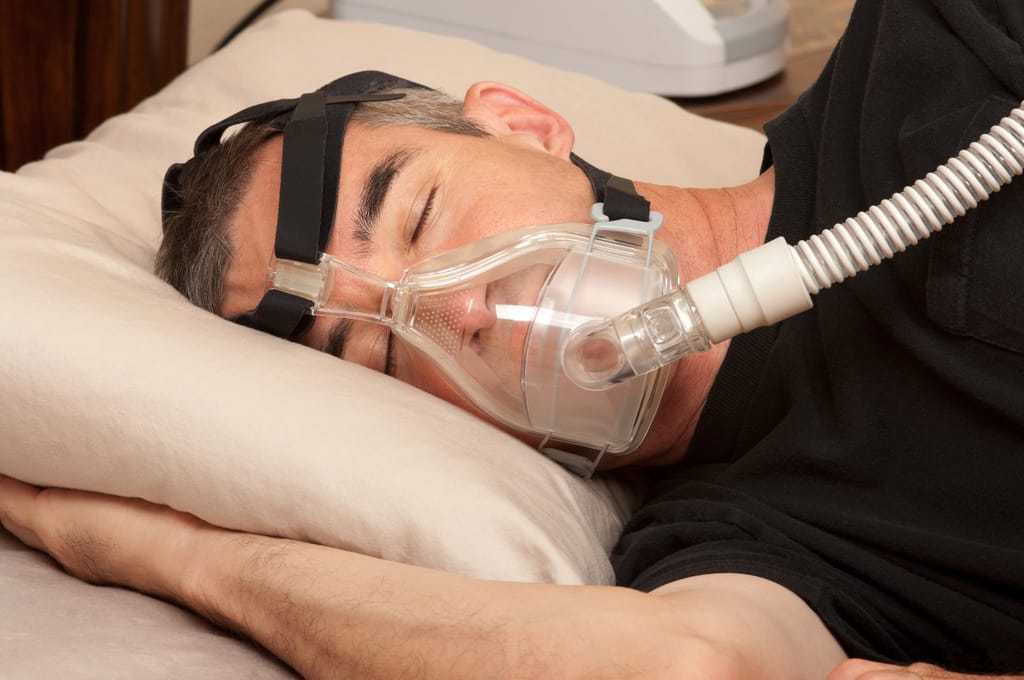
Treatment
The most common treatment for sleep apnea is continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy. This involves wearing a mask that delivers a continuous stream of air through the nose and mouth while sleeping to keep the airway open. It is the most effective treatment for sleep apnea and is often covered by health insurance.
Other treatments for sleep apnea include oral appliances, which are worn in the mouth during sleep to help keep the airway open. These devices can be prescribed by a dentist or orthodontist. Surgery is also an option for some people, although this is usually only recommended in more severe cases.
Lifestyle modifications can also be helpful in managing sleep apnea. These include losing weight, avoiding alcohol and sleeping pills, and sleeping on the side rather than the back. Quitting smoking is also important, as smoking can worsen the symptoms of sleep apnea. In addition, some people may benefit from practices such as yoga and meditation, which can help to relax the body and reduce stress.
Conclusion
Sleep apnea is a serious disorder that is characterized by repeated pauses in breathing during rest. These pauses can last for several seconds or minutes and can occur up to 30 times per hour. Each time you stop breathing, the level of oxygen in your blood drops. This can lead to a number of health problems, including heart disease, high blood pressure, and stroke.
Reference
- Sleep apnea – Symptoms and causes. (2022, December 23). Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/sleep-apnea/symptoms-causes/syc-20377631
- Sleep Apnea: What It Is, Causes, Symptoms & Treatment. (n.d.). Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/8718-sleep-apnea
- Sleep Apnea. (2022, July 18). Johns Hopkins Medicine. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/sleep-apnea